메소드란
- 블랙박스라고 한다. 매개변수 파라미터로 값을 전달받고 어떤 연산을 수행한 후 결과값을 돌려준다.
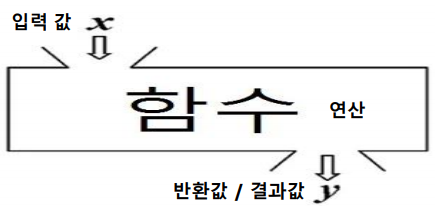
표현식
[접근제한자][예약어] 반환형 메소드명(매개변수){
//실행내용 작성
}
메소드의 접근제한자
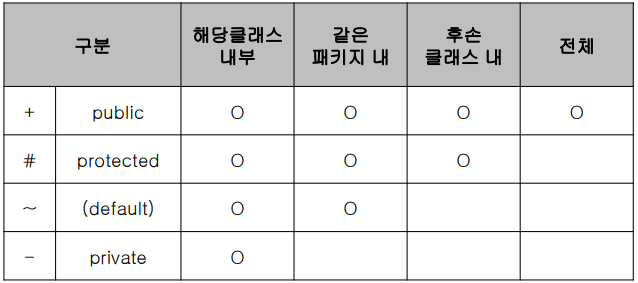
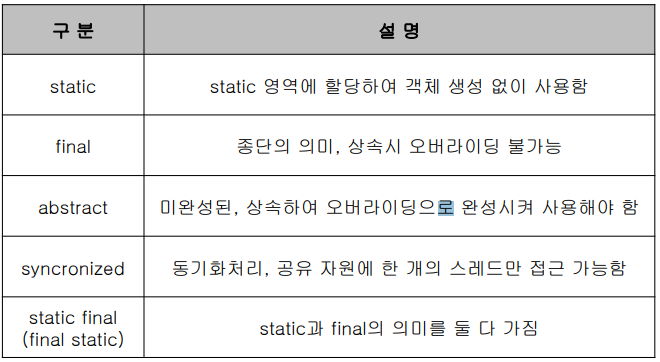
메소드의 예약어
- public void test(); - 미완성된 메소드인데 abstract 상속을 했을때 오버라이딩을 하기위한 강제성을 지닌다.
메소드의 반환형
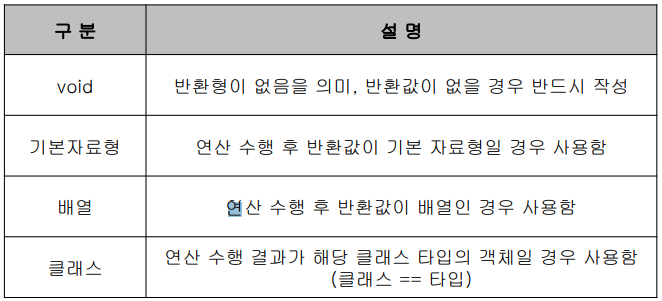
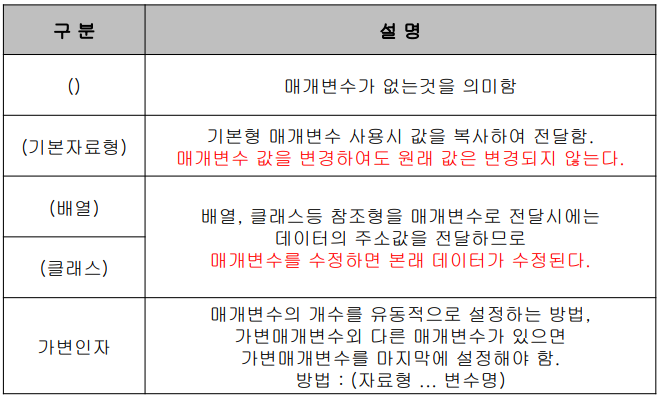
메소드의 매개변수
- 가변인자 : (자료형 ... 변수명) 배열
- 예) main method(String[] args)의 매개변수처럼
오버로딩
- 한 클래스 내에서 파라미터선언부(매개변수)가 다르고, 이름이 같은 메서드를 여러 개 정의하는 것.
오버로딩 성립조건
- 메소드 이름이 같아야한다.
- 매개변수 선언부가 달라야한다.
- 매개변수 타입, 개수 , 순서
오버로딩 주의점
- 매개변수명은 상관치 않는다.
- 리턴타입은 오버로딩시 상관치 않는다.
public class TestOverloading {
public int test() {
return 0;
}
public int test(int a) {
return 0;
}
public int test(int a, int b) {
return 0;
}
public int test(int a, String s) {
return 0;
}
//에러 발생
//매개변수명은 상관 없이 자료형의 개수와 순서가 다르게 작성되어야 한다.
/*public int test(int b, int a) {
return 0;
}*/
public int test(String s, int a) {
return 0;
}
public String test(int a, int b, String str) {
return null;
}
//에러발생
//리턴타입이 다르다고 오버로딩이 적용되지 않는다.
/*public int test(int a, int b, String str) {
return 0;
}*/
//에러발생
//접근제한자가 다르다고 오버로딩이 적용되지 않는다.
/*private String test(int a, int b, String str) {
return "";
}*/
}
메소드의 종류
- 매개변수 유무와 반환값 유무에 따른 구분
- Non-static 메소드
NonStaticMethodTest
//1. 매개변수가 없고 반환값이 없는 메소드
public void method1() {
//아무 값도 반환하지 않고 메소드 내용만 수행한 후 리턴값이 없이 호출한 메소드로 돌아간다.
System.out.println("매개변수와 반환값이 둘 다 없는 메소드 입니다.");
return; //모든 메소드에 생략되어 있음(JVM이 자동 생성)
}
//2. 매개변수가 없고 반환값이 있는 메소드
public String method2() {
return "매개변수가 없지만 반환값이 있는 메소드입니다.";
}
//3. 매개변수가 있고 반환값이 없는 메소드
public void method3(int num1, int num2) {
//호출하는 쪽의 괄호에 인자로 넘긴 값을 받기 위해 선언하는 것이 매개변수이며
//메소드 선언 시 괄호 안에 변수를 선언하여 메소드 내에서 사용한다.
int sum = num1 + num2;
System.out.println("sum : " + sum);
return;
}
//4.매개변수가 있고 반환값이 있는 메소드
public int method4(int num1, int num2) {
return num1 + num2;
}
2. static 메소드
StaticMethodTest
public class StaticMethodTest {
//static 메소드는 정적(static)메모리 공간에 프로그램 실행 시 저장된다.
//또한 프로그램 종료 시 정적 메모리 영역에서 삭제된다.
//매개변수가 없는 메소드
//1. 리턴값이 없을때
public static void staticMethod1() {
int num1 = 10;
int num2 = 20;
System.out.println("10과 20의 합은 " + (num1 + num2) + "입니다.");
}
//2. 리턴값이 있을때
public static int staticMethod2() {
int num1 = 10;
int num2 = 20;
return num1 + num2;
}
//매개변수가 있는 메소드
//1. 리턴값이 있을때
public static void staticMethod3(String name) {
System.out.println(name + "님의 방문을 환영합니다.");
}
//2. 리턴값이 없을때
public static String staticMethod4(String name) {
return name + "님의 방문을 환영합니다.";
}
}
Run
package com.kh.chap05_method.part02_methodTest;
import static com.kh.chap05_method.part02_methodTest.StaticMethodTest.*;
public class Run {
public static void main(String[] args) {
NonStaticMethodTest test = new NonStaticMethodTest();
test.method1();
//매개변수가 없고 반환값이 있는 메소드 호출의 경우
//리턴타입과 일치하는 자료형의 변수에
//메소드 수행 결과를 담아서 사용한다.
/*String str = test.method2();
System.out.println(str);*/
System.out.println(test.method2());
//매개변수가 있고 반환값이 없는 메소드의 호출의 경우
//반드시 인자로 매개변수의 타입, 개수, 순서가 일치하는 값을 넘겨줘야 한다.
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
test.method3(a, b); //전달값(인자 = argument)이 공간(매개변수 = parameter)으로 넘어간다. ***면접질문
int result = test.method4(10, 20);
System.out.println("result : " + result);
//static 메소드 호출시에는 객체를 생성하지 않고 호출한다.
//사용방법은 클래스명.메소드명()으로 사용한다.
//클래스명을 사용하지 않으려면 static import를 해야한다.
//import static 패기지명.클래스명.*;
/*StaticMethodTest.*/staticMethod1();
System.out.println("10과 20의 합은 " + StaticMethodTest.staticMethod2() + "입니다.");
StaticMethodTest.staticMethod3("김진호");
System.out.println(StaticMethodTest.staticMethod4("홍길동"));
}
}
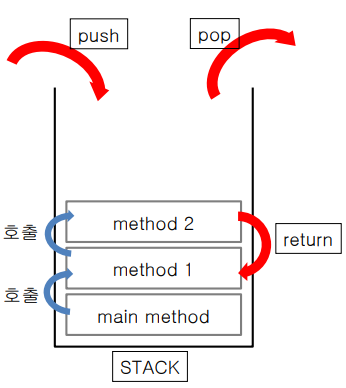
return
- return이란 해당 메소드를 종료하고, 자신을 호출한 메소드로 돌아가는 예약어이다.
- 반환값(리턴값)을 가지고 자신을 호출한 메소드로 돌아갈 수 있다.
- main() 메소드에서의 지역변수를 method1()이 알 수 없지만 매개변수를 사용하면 값을 전달 받을 수 있다. ( ( ) 는 통로역할을 한다.)
- LIFO(Last-Input-First-Out)
getter와 setter 메소드
- getter
- 필드에 변경할 값을 전달 받아서 필드값을 변경하는 메소드
접근제한자 void set필드명(자료형 변수) {
(this.)필드명 = 매개변수;
}- setter
- 필드에 기록된 값을 읽어서 요구하는 쪽으로 읽은 값을 넘기는 메소드
접근제한자 반환형 get필드명() {
return 필드명;
}
실습문제 7
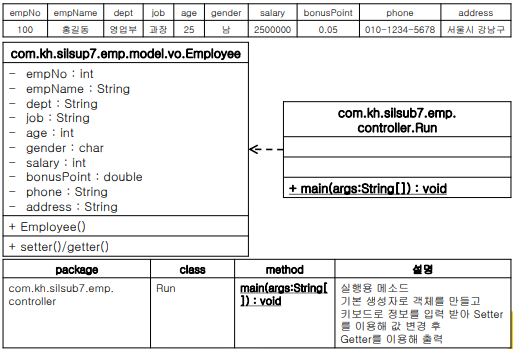
Employee
public class Employee {
private int empNo;
private String empName;
private String dept;
private String job;
private int age;
private char gender;
private int salary;
private double bonusPoint;
private String phone;
private String address;
public Employee() {}
//setter
public void setEmpNo(int empNo) {
this.empNo = empNo;
}
public void setEmpName(String empName) {
this.empName = empName;
}
public void setDept(String dept) {
this.dept = dept;
}
public void setJob(String job) {
this.job = job;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public void setGender(char gender) {
this.gender = gender;
}
public void setSalary(int salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
public void setBonusPoint(double bonusPoint) {
this.bonusPoint = bonusPoint;
}
public void setPhone(String phone) {
this.phone = phone;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
//getter
public int getEmpNo() {
return empNo;
}
public String getEmpName() {
return empName;
}
public String getDept() {
return dept;
}
public String getJob() {
return job;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public char getGender() {
return gender;
}
public int getSalay() {
return salary;
}
public double getBonusPoint() {
return bonusPoint;
}
public String getPhone() {
return phone;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
}Run
public class Run {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Employee e = new Employee();
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("empNo 입력 : ");
e.setEmpNo(sc.nextInt());
sc.nextLine();
System.out.print("empName 입력 : ");
e.setEmpName(sc.nextLine());
System.out.print("dept 입력 : ");
e.setDept(sc.nextLine());
System.out.print("job 입력 : ");
e.setJob(sc.nextLine());
System.out.print("age 입력 : ");
e.setAge(sc.nextInt());
System.out.print("gender 입력 : ");
e.setGender(sc.next().charAt(0));
System.out.print("salary 입력 : ");
e.setSalary(sc.nextInt());
System.out.print("bonusPoint 입력 : ");
e.setBonusPoint(sc.nextDouble());
System.out.print("phone 입력 : ");
sc.nextLine();
e.setPhone(sc.nextLine());
System.out.print("address 입력 : ");
e.setAddress(sc.nextLine());
System.out.print(e.getEmpNo() + ", ");
System.out.print(e.getEmpName() + ", ");
System.out.print(e.getDept() + ", ");
System.out.print(e.getJob() + ", ");
System.out.print(e.getAge() + ", ");
System.out.print(e.getGender() + ", ");
System.out.print(e.getSalay() + ", ");
System.out.print(e.getBonusPoint() + ", ");
System.out.print(e.getPhone() + ", ");
System.out.print(e.getAddress() + ", ");
}
}
재귀호출(recursive call)
- 메소드 내에서 본인 메소드를 다시 호출하는 것을 재귀호출이라고 한다.
public class RecursiveCallTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
RecursiveCallTest test = new RecursiveCallTest();
int result = test.factorial(5);
System.out.println(result);
}
public int factorial(int num) {
if(num == 1) {
return 1;
}else {
return num * factorial(num - 1); //재귀호출
}
}
}'JAVA > 이론 정리 및 예제' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [JAVA/자바] #9_1 다형성 / 예제 (0) | 2021.09.17 |
|---|---|
| [JAVA/자바] #8_1 상속 / 예제 (0) | 2021.09.17 |
| [JAVA/자바] #6_4 생성자(constructor) / 예제 (0) | 2021.09.14 |
| [JAVA/자바] #6_3 필드(field)/ 예제 (0) | 2021.09.14 |
| [JAVA/자바] #6_2 클래스 (0) | 2021.09.14 |